
Qué es la gestión del talento y por qué es necesaria

Introducción
Organizations are now more aware than ever that their success largely depends on their workforce. It has led to a renewed focus on talent management as an essential business function.
Effective talent management ensures the right people are in the right roles and helps improve employee performance, increase productivity, and reduce turnover. A strategic HR team helps.
Staying in touch with the latest talent management industry trends and strategies is crucial. Whether it’s implementing a talent management system, adopting best practices for performance management, or developing a comprehensive talent management strategy, there are many ways to improve your organization’s efforts.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the importance of talent management in today’s business environment and discuss some of the key talent management trends.
What is Talent Management?
Talent management refers to attracting, identifying, developing, and retaining gifted workers to achieve organizational goals. A practical talent management framework aims to ensure that an organization has the right people in the right positions with the necessary skills and knowledge to drive business success. A successful talent management strategy involves HR professionals creating a streamlined approach that exercises proper HR management principles which align with the organization’s business operations.
Talent Management Example
One common talent management solution sees identifying high-potential employees and providing them with skills development opportunities to prepare them for future leadership roles.
It can involve creating a leadership development program that includes coaching, mentoring, and training in areas such as strategic thinking, decision-making, and communication.
By investing in developing high-performing employees, organizations can ensure a pipeline of strong leaders equipped to guide the organization through future challenges and opportunities. This approach also helps foster a culture of continuous learning and development, improving overall staff retention and productivity.

Source: HR Grapevine
Key Principles of Talent Management
One key aspect of talent management is performance management, which involves setting performance expectations, monitoring employee performance, providing feedback, and taking action to improve performance when necessary. A robust system ensures that current employees meet their business goals and contribute to the organization’s overall success.
Another feature of developing successful talent management systems is having a solid pathway for talent acquisition. The human resources department should be designed to identify and nurture talent at all levels of the organization, from entry-level positions to top leadership roles. They should be well-versed in rapid talent allocation.
Talent management involves developing a positive employee experience and engaging work environment that fosters the employee journey and retention. It may include providing competitive compensation and benefits packages, promoting work-life balance, offering career growth and developing talented employees.
A successful talent strategy is crucial in building a resilient workforce that can respond to changing market conditions and drive innovation.

Source: Research Gate
Why is Talent Management Important?
Organizations can attract, develop, and retain the best talent by developing a comprehensive talent management strategy and creating a high-performance and continuous improvement culture.
The best talent management strategies are those run by organizations that invest in developing and engaging their workforce, and these businesses tend to experience more significant innovation and profitability. On the other hand, companies that need help attracting or retaining top employees often face challenges such as low customer satisfaction and limited growth opportunities.
Benefits of Implementing Talent Management Into Your Organization

Source: Human Resource Management
- Improved Recruitment: Talent management ensures that the organization attracts and hires the right people for the job, resulting in better quality hires and lower recruitment costs.
- Increased Retention: By investing in employee development and engagement, talent management helps reduce turnover and retain top performers, which leads to cost savings and a more stable workforce.
- Better Employee Performance: A robust system includes performance management practices that help employees set and achieve goals, receive regular feedback, and develop skills to improve performance.
- Succession Planning: By identifying and developing high-potential employees, the process helps to ensure a pipeline of qualified candidates for key leadership roles.
- Improved Innovation: A diverse and skilled workforce, supported by a culture of innovation, can drive creativity and new ideas within the organization.
- Enhanced Company Culture: Best practices that foster employee engagement, recognition, and development contribute to a positive and supportive company culture that can improve overall job satisfaction and productivity.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: A skilled and engaged workforce can improve customer service and satisfaction, leading to greater customer loyalty and retention.
- Competitive Advantage: By attracting and retaining top talent, organizations can gain a competitive advantage, increasing market share and profitability.
- Cost Savings: By reducing turnover, improving performance, and identifying and developing high-potential employees, a talent management strategy can lead to cost savings in recruitment, training, and development.
- Better Decision-Making: By developing and nurturing talent at all levels of the organization, a talent management strategy can result in a more knowledgeable and skilled workforce, leading to better decision-making and overall business performance.
The Talent Management Model

Source: Expert 360
While there are many talent management models, the essential elements of talent management can generally be categorized into five phases.
Planning
The planning stage is comprised of three key areas.
- Understanding the organizational/business strategy
- Evaluation and measurement/analytics
- Developing a workforce plan
The first phase involves identifying the organization’s needs and developing a talent management strategy aligning with the company’s goals and objectives.

Sample Workforce Plan – Source: Expert 360
Attracting
The attracting stage is comprised of four focus points:
- Employee Value PropositionD
- Marketing
- Adquisición de talentos
- Consultants/Freelancers
The second phase involves attracting potential candidates to the organization. It includes building a strong employer brand, creating effective recruitment strategies, and designing job descriptions that attract suitable candidates.
Developing
The developing phase consists of five areas on which to focus:
- Onboarding performance
- Appraisals/management
- Aprendizaje y desarrollo
- Capability frameworks
- Career pathways
The organization develops the skills and knowledge of employees to ensure they are equipped to perform their jobs effectively by providing coaching, mentoring, and other job-specific training.

Development of an EVP – Source: Experto 360
Retaining
The retention phase consists of two main focus points:
- Culture
- Remuneration strategy
The retention phase emphasizes retaining top talent and reducing employee turnover. It can be achieved by offering competitive compensation and benefits packages, creating a positive work environment, and providing career growth and advancement opportunities.
Transitioning
The final phase of the model consists of five important considerations:
- Planificación de la sucesión
- Internal mobility
- Retirement
- Knowledge management
- Exit interviews
Transitioning means identifying and developing future leaders within the organization. It includes identifying high-potential employees, providing development programs to prepare them for leadership roles, and creating a succession plan to ensure a smooth transition when key employees leave the organization.
The Talent Management Process
The talent management model (TMM) and the talent management process (TMP) are different approaches to managing talent in an organization.
The TMM is a comprehensive framework that outlines the key components. It provides a strategic roadmap for building a strong and resilient workforce and aligning organizational objectives with business outcomes.
On the other hand, the TMP is a set of sequential stages that organizations typically follow to manage their talent, from identifying talent needs to retaining top performers.
While the TMM provides a high-level view of the talent management process, the TMP provides a more detailed, step-by-step approach to talent management strategies.

Talent management software users – Source: Capterra
The TMP generally includes the following stages:
- Workforce planning: The first stage considers identifying the organization’s current and future talent needs based on business objectives and developing a plan to meet those needs.
- Attracting talent: This stage requires sourcing and attracting potential candidates through various channels such as job boards, social media, and employee referrals.
- Selection: In this stage, the organization assesses candidates’ qualifications, skills, and experience and selects the best candidate for the job.
- Onboarding: Once a candidate is selected, the organization provides the necessary information, tools, and resources to become productive team members.
- Performance management: This stage involves setting performance goals, giving feedback, and assessing performance regularly.
- Development and training: This stage compels HR leaders to identify employees and existing talent that require employee training and provide them with the necessary learning and development opportunities to learn new skills to help enable employees.
- Succession planning: This stage involves identifying high-potential employees and preparing them for leadership positions to ensure a smooth transition when key employees leave the organization.
- Retention: As the name suggests, the last step refers to retaining talent and implementing talent management strategies to reduce employee turnover, maintain a motivated workforce and deliver employee benefits.
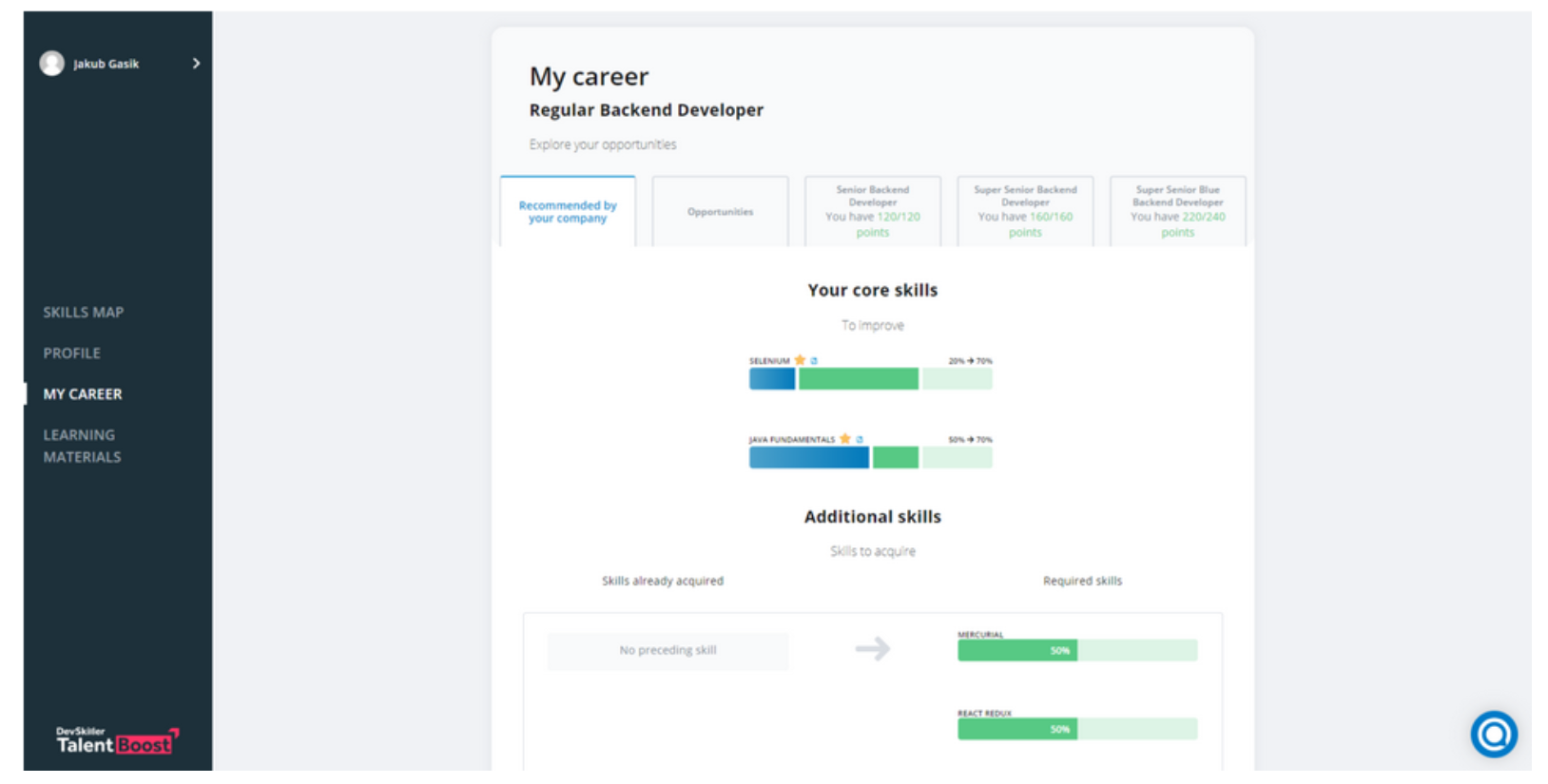
How DevSkiller Talent Boost Can Help Your Organization
DevSkiller TalentBoost can help with talent management by providing an all-in-one platform for attracting, assessing, developing and retaining high-quality employees.
With its suite of tools for candidate sourcing, skills testing, and personalized learning, TalentBoost enables organizations to identify high-potential candidates, assess their skills and competencies, track progress, and provide targeted training and emphasis on developing new hires.
TalentBoost’s skills assessments provide an objective and unbiased way to evaluate candidates’ technical skills, enabling organizations to make data-driven hiring decisions and identify candidates who best fit the job. The platform’s personalized learning paths help employees build their skills and stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and industry trends, improving their job performance and satisfaction.
Overall, TalentBoost streamlines the TMP, enabling organizations to attract, assess, and develop new employees and in-house talent more efficiently and effectively, ultimately driving business success and achieving strategic objectives.
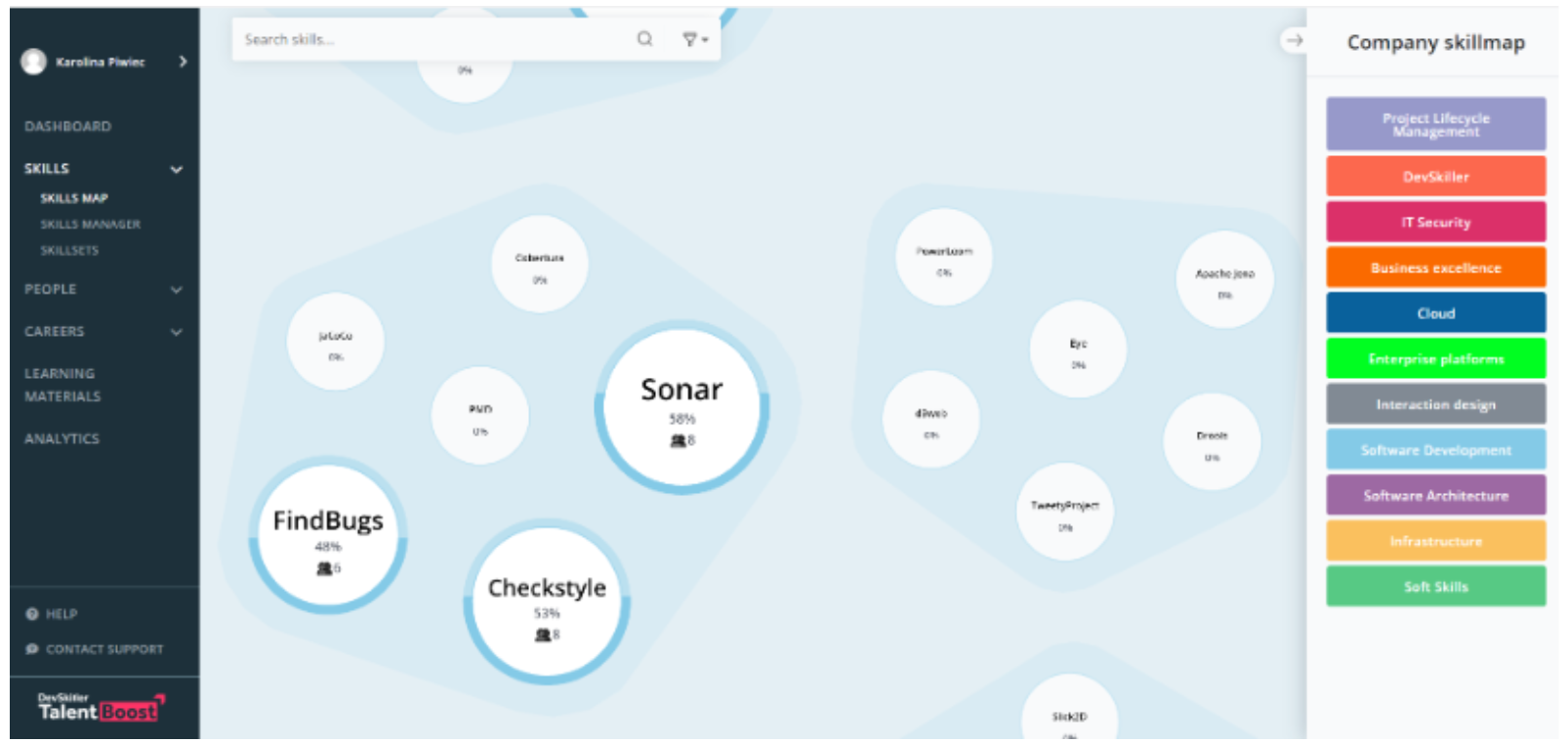
Resumen
Upon discovering the advantages of talent management, you should examine why investing in it is crucial and pinpoint which areas in your business require improvement.
Additionally, you can evaluate the different components of talent management and identify which ones suit your organization. Developing a personalized strategy aligned with your company’s goals and objectives is vital.
Keep in mind that your success relies on having access to the right talent. You can begin your journey to acquire the ideal candidates by using the resources available here.
Find out more about DevSkiller TalentBoost
Fuente de la imagen: ICMA




